Hey friends welcome to the new post of all about electronics and today we will see the source transformation in the network analysis. so this is very useful technique in solving the problems with the network analysis using this source transformation we can simplify any circuit in the network in the network analysis.
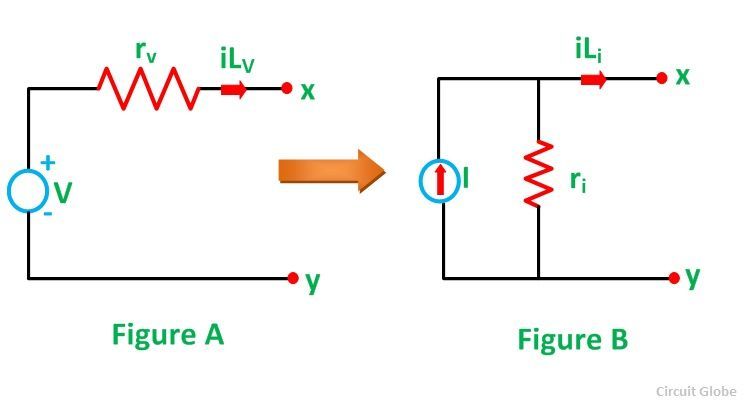
So as its name suggests it is related to the source and the source is here nothing but voltage and the current. So, using this source transformation we can convert any voltage source into the current source for a vice versa any current source into the voltage source.So, let's say we have one voltage source Vs with a series resistance R, which is connected to a some network via terminal AB. So using this source transformation we can convert this voltage source into the current source Is with the same resistance R in a parallel with this current source.
Likewise if we have a current source Is with resistance R in a parallel in any network then that can be converted into the voltage source Vs with the same resistance R in a series with this voltage source. So, here during the transformation the characteristic of the network not get changed that means the voltage across this terminal AB and the current that is entering into this node A will remain the same after the transformation. So, let's say that voltage across these two terminal AB is Vx and the current that is entering into this node a is Ix. So, we can write Vx= Vs-(Ix*R). That is drop across this resistance R.
Similarly for the transform network, voltage across these two terminal will remain the same that is Vx. And the current that is entering into this node A will remain the same, that is Ix after the transformation. So here we can write V X is nothing but drop across this resistor R. Let's say that is(I*R). where current I is the current that is flowing through this resistor R. So here I is nothing but Is-Ix. So, we can write V X as (Is-Ix)*R. That is nothing but
Vx= Is*R - Ix*R .
Now here we can compare these two equations. So we will get
Vs- Ix*R=Is*R- Ix*R
So, this two term will cancel out. So we will get
Vs=Is*R or we can write Is=Vs/R
So, here in this way we get a relationship between the voltage and the current. So, if we have a voltage source Vs with a series resistors R in a network that can be transformed into the current source Is with the same resistance R in parallel with this current source. And the value of this current source will be nothing but Vs/R Let us take one example let's say we have a 30 volt voltage source with resistance of 10 ohm in series that is connected to a some Network so we can transform this voltage source into the current source with the same 10 ohm resistor in a parallel with its current source.
So, the value of this current source I will be given as V/R Tthat is nothing but a 3 ampere.So in this way we can transform this 30 Volt voltage source into a 3 ampere current source with a 10 ohm resistor in a parallel. Likewise, let's say we have a current source Is with a resistance R in a parallel in any network that can be transformed into the voltage source Vs with the same resistor R in a parallel.
The value of this voltage source Vs is nothing but Is*R. so let us take one example. Let's say we have a 1A current source with 10 ohm resistor in a parallel. So we can transform this current source into the voltage source with the same 10 ohm resistor in a series with this voltage source. The value of this voltage source V is given by I*R that is nothing but 10 volt So, in this way we can transform this 1 ampere current source into the 10 V voltage source. So, now let's take a one numerical and find the usefulness of this source transformation in simplifying the circuit.So, here we have a one circuit.
And in this circuit we need to find a voltage across this 2 ampere current source. Let's say the voltage across this 2 ampere current source is Vx. We need to find the voltage across this 2 ampere current source. So just by looking at the circuit it looks bit complicated find a voltage across this 2 ampere current source. But we will see that using the source transformation we can easily find out the voltage across this 2 ampere current source.
So, first of all, let's just concentrate on this left portion of the circuit. Here we have a volt voltage source which is connected the 6 ohm resistor in a series. So we can transform this voltage source into the current source so that we have a this ohm resistor and 12 ohm resistor arein a parallel. So, first of all, let's just transform this 4 volt voltage source into the current source.
So, in the equivalent circuit we will have a current source with a same 6 oh resistor in a parallel. And the value of this current source I is nothing but V upon R that is 4/6 that is 2 by 3 ampere.So, in this way we can transform this 4V voltage source into these 2 / 3 ampere current source. so we will have a 2 / 3 ampere current source with a 6 ohm resistor in a parallel in the equivalent circuit. So, now here as you can see now we have this 6 ohm resistor and 12 resistors are in a parallel. So, here the equivalent resistance is let us say Rp and it is given by 6 ohm in parallel with 12 ohm that is nothing but (6*12)/(6+12) which is nothing but a 4 ohm.
Here we can replace these two resistance by their equivalent parallel resistance. So the equivalent circuit now will have a 2/ 3 ampere current source is the 4 ohm resistor in a parallel. so now here again as you can see we can transform this current source into the voltage source so that we have this 8 volt voltage source with this transformed voltage source in a series. So, now let's convert this current to the voltage source. So, here now we have a 2 /3 ampere current source with 4 ohm resistor in a parallel. So, they're equivalent transform source will have a voltage source with 4 ohm resistor in a series.
And the value of this voltage source V is given by I*R. That is 2 by 3 into 4 ohm.That that is nothing but 8 by 3 volt. So we can replace this 2 by 3 ampere current source into this 8 by 3 word voltage source.And the equivalentcircuit now we'll have a 8 by 3 volt voltage source with 4 ohm resistor in a series that is connected to this 8 volt voltage source.So, now here we have this 8/3 volt voltage source in series with this 8 volt voltage source. so we can replace it with a single equivalent voltage source so we will have now 8+8/3 that is 32 / 3 volt.
We can replace these two voltage sources by this 32 / 3 volt voltage source. So the equivalent circuit now will look like this. Now we have this 32/ 3 volt voltage source in series with this for ohm resistor. So, here again now we can convert this voltage source into the current source so that this 4 ohm and 12 register will come in parallel. And we can simplify this circuit. so here this 32/3 volt voltage source can be converte into the current source with this 4 ohm resistor in a parallel.And the value of the current source I is nothing but V upon R that is (32 /3)/4. which comes out to be a 8 / 3 A. So, we can replace this voltage source with their equivalent current source.
And the equivalent current equivalent circuit now will look like this. It has a 8 / 3 ampere current source with 4 ohm resistor in a parallel. So as you can see now we have the 4 ohm and 12 ohm resistor are in a parallel. so we can replace these two registers by their equivalent parallel resistance. Let's say it is Rp and it is given by 4 ohm parallel 12 ohm that is nothing but (4*12)/(4+12) which comes out to be a 3 ohm so we can replace these two resistors by their equivalent parallel resistance 3 ohm.
Now the circuit will have a 3 ohm resistor in parallel with this two current sources. And the voltage across these 2 ampere current source is nothing but the voltage drop across this 3 ohm resistor. So, Vx can be given as 3 * I where I is nothing but a current that is passing through this 3 ohm resistor. so value of I is given as 2 ampere minus 8/3 ampere. And it comes out to be a - 2/3 ampere. so we can write this I as - 2/3 ampere.So we will VX =-2 volt So, in this way using the source transformation we can easily simplify any circuit and find the parameters in the any circuit.
So I hope you understood what is source transformation and how it is useful in simplifying the any network or circuit the link is provided in the description below to download more such examples based on the source transformation and if you want the solution for the same please let me know in the comment section below.

إرسال تعليق